Day 22: Binary Search Trees
Hey CodingHumans today, we're working with Binary Search Trees (BSTs).
Binary Search Tree
A Binary Search Tree (BST), , is a binary tree that is either empty or satisfies the following three conditions:
Each element in the left subtree of t is less than or equal to the root element of t (i.e., max(leftTree(t).value<=t.value ).
Each element in the right subtree of t is greater than the root element of (i.e., min(rightTree(t).value>t.value ).
Both leftTRe(t) and rightTree(t) are BSTs.
You can essentially think of it as a regular binary tree where for each node parent having a leftChild and rightChild, leftChid.value<=parent.value<rightChaid.value . In the diagram above, the binary tree of integers on the left side is a binary search tree.
Task
The height of a binary search tree is the number of edges between the tree's root and its furthest leaf. You are given a pointer, , pointing to the root of a binary search tree. Complete the getHeight function provided in your editor so that it returns the height of the binary search tree.
Input Style
The locked stub code in your editor reads the following inputs and assembles them into a binary search tree:
The first line contains an integer, , denoting the number of nodes in the tree.
Each of the subsequent lines contains an integer, , denoting the value of an element that must be added to the BST.
Output Style
The locked stub code in your editor will print the integer returned by your getHeight function denoting the height of the BST.
Sample Input
7
3
5
2
1
4
6
7
Sample Output
3
Explanation
The input forms the following BST:
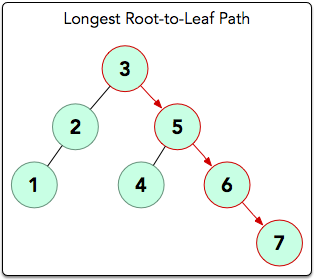
The longest root-to-leaf path is shown below:
There are 4 nodes in this path that are connected by 3 edges, meaning our BST's height=3. Thus, we print 3 as our answer.
Recommended: Please try your approach on your integrated development environment (IDE) first, before moving on to the solution.
Few words from CodingHumans : Don't Just copy paste the solution, try to analyze the problem and solve it without looking by taking the the solution as a hint or a reference . Your understanding of the solution matters.
HAVE A GOOD DAY 😁
Solution
( Java )
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
class Node{
Node left,right;
int data;
Node(int data){
this.data=data;
left=right=null;
}
}
class Solution{
public static int getHeight(Node root){
int heightleft=0;
int heightright=0;
if(root.left!=null){
heightleft=getHeight(root.left)+1;
}
if(root.right!=null){
heightright=getHeight(root.right)+1;
}
return (heightleft>heightright?heightleft:heightright);
}
public static Node insert(Node root,int data){
if(root==null){
return new Node(data);
}
else{
Node cur;
if(data<=root.data){
cur=insert(root.left,data);
root.left=cur;
}
else{
cur=insert(root.right,data);
root.right=cur;
}
return root;
}
}
public static void main(String args[]){
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int T=sc.nextInt();
Node root=null;
while(T-->0){
int data=sc.nextInt();
root=insert(root,data);
}
int height=getHeight(root);
System.out.println(height);
}
}
If you have any doubts regarding this problem or need the solution in other programming languages then leave a comment down below .